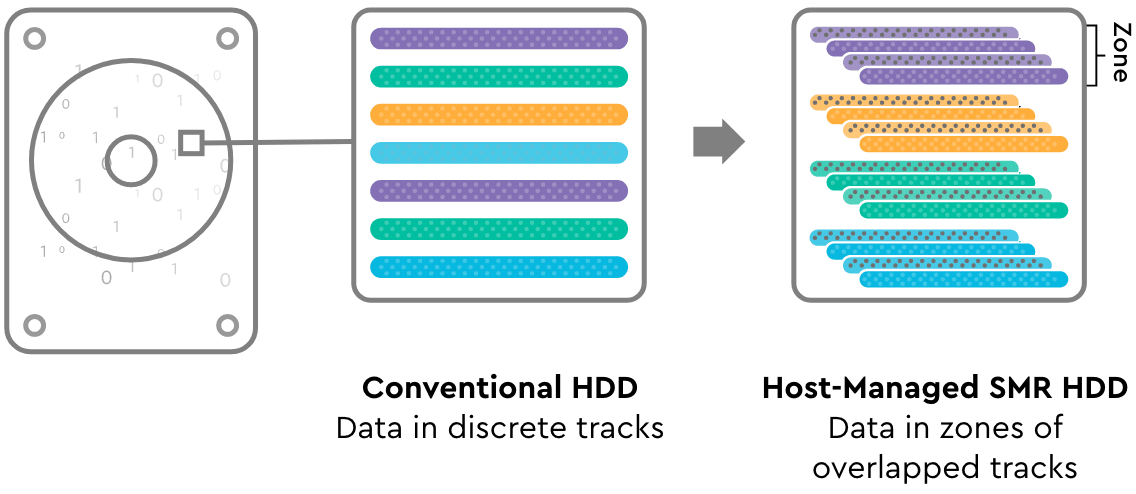
Zoned Storage
Higher Capacities, Lower TCO & Improved QoS
The Increasing demand for data center storage capacities
Data volumes created by enterprises, machines, and consumer-generated content continue to drive demand for data center storage capacities at petabyte, exabyte and even zettabyte scale. Today, large scale data infrastructure already uses tens of thousands of SSDs and HDDs. Managing the extreme scale of data in a cost-effective manner is quickly becoming a requirement.
Zoned storage devices, such as ZNS SSDs are divided into zones, significantly simplifying the drive architecture and minimizing the need for complex data management. With a unified software stack, the host is able to intelligently place data in different zones which enables these key benefits:

Increased Capacities
Higher density and scale as virtually no over-provisioning is required
Reduced Cost
Significantly reduced DRAM requirements and fewer support logic functions are required
Improved QoS
With minimal garbage collection required, the device controller can respond quicker

Increased Endurance
Because the data is not constantly re-written, the endurance is improved
The act of implementing Zone Storage on the host allows the system software and hardware to work together more efficiently by eliminating the multiple (duplicated) levels of indirection required for logical to physical mapping between the host and the SSD controller and the file system to the device. ZNS also reduces the need for over-provisioning and removes the issues associated with write amplification and QoS variability. In short ZNS addresses the issues of scale, QoS and TCO which hinder conventional SSDs.
With a unified software framework, data can be intelligently placed on both SMR HDDs and ZNS SSDs to increase storage capacity, lower TCO and improve QoS. With Zoned Storage, data center and cloud providers can more cost effectively scale storage for the zettabyte age.
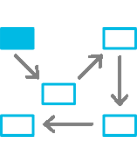
Conventional
Device controls data placement


Zoned
Applications control data placement in zones
Achieving Increased Capacities Through Zoned Storage
Featured Articles
Forward Looking Statements
This webpage may contain forward-looking statements, including, but not limited to, statements regarding our product and technology portfolio, the capacities, capabilities and applications of, and market for, our products, our strategies and growth opportunities, and market trends. These forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed in or implied by the forward-looking statements. The risks and uncertainties are discussed more fully in Western Digital Corporation’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including our most recently filed periodic report, to which your attention is directed. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements and we undertake no obligation to update these forward-looking statements to reflect subsequent events or circumstances, except as required by law.
Disclosures
1. Source 1: What is Zoned Storage and Why Does it Matter by William G. Wong (Electronic Design, 9/20/2020)
2. Source 2: The Next Step in SSD Evolution: NVMe Zoned Namespaces Explained by Billy Tallis (AnandTech.com, 8/6/2020)